HDD vs SSD Hosting: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of web hosting, the type of storage you choose for your website can significantly impact its performance, speed, and reliability. Two popular storage options are HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive). Understanding the differences between these two types of storage can help you make an informed decision for your hosting needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is HDD Hosting?
- What is SSD Hosting?
- Key Differences Between HDD and SSD
- Pros and Cons of HDD Hosting
- Pros and Cons of SSD Hosting
- Performance Comparison
- Cost Considerations
- Use Cases for HDD Hosting
- Use Cases for SSD Hosting
- Making the Right Choice for Your Website
- Conclusion
Introduction
Choosing the right hosting solution is crucial for the success of your website. This article will explore the differences between HDD and SSD hosting, helping you understand which option might be best for you.
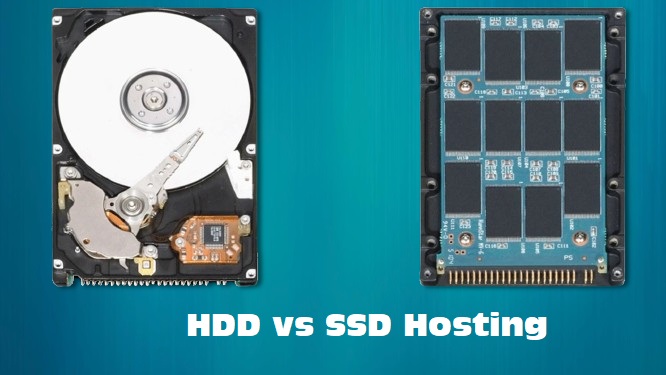
What is HDD Hosting?
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) hosting uses traditional mechanical drives to store and retrieve data. These drives have been around for decades and are known for their large storage capacities at relatively low costs.
Key Features of HDD
- Mechanical Components: HDDs use spinning disks to read/write data.
- Capacity: Typically offers more storage space compared to SSDs.
- Cost: Generally cheaper than SSDs.
- Speed: Slower data access speeds due to mechanical parts.
What is SSD Hosting?
SSD (Solid State Drive) hosting uses flash memory to store data, providing faster data access speeds and improved performance compared to HDDs.
Key Features of SSD
- No Moving Parts: SSDs use NAND flash memory, making them more durable.
- Speed: Significantly faster data access and retrieval speeds.
- Reliability: Less prone to mechanical failure.
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes less power compared to HDDs.
Key Differences Between HDD and SSD
| Feature | HDD Hosting | SSD Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower due to mechanical parts | Faster due to flash memory |
| Durability | Prone to mechanical failure | More durable with no moving parts |
| Cost | More affordable | Generally more expensive |
| Storage Capacity | Higher storage capacities available | Typically lower storage capacities |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Noise | Can be noisy | Silent operation |
Pros and Cons of HDD Hosting
Pros
- Cost-Effective: HDDs are generally cheaper, making them a budget-friendly option.
- Large Storage Capacity: Ideal for storing large amounts of data.
Cons
- Slower Performance: The mechanical parts limit data access speeds.
- Higher Failure Rate: More prone to mechanical failures.
Pros and Cons of SSD Hosting
Pros
- High Performance: Faster data access and retrieval.
- Durability: No moving parts, less likely to fail.
- Energy Efficient: Consumes less power.
Cons
- Cost: More expensive compared to HDDs.
- Limited Storage Capacity: Typically offers less storage space.
Performance Comparison
When it comes to performance, SSDs have a clear advantage over HDDs. Here’s why:
Speed
- Boot Time: Websites hosted on SSDs load faster.
- Data Access: SSDs provide quicker read/write speeds, enhancing overall performance.
Reliability
- Lifespan: SSDs have a longer lifespan due to the absence of moving parts.
- Failure Rate: Lower compared to HDDs, which are prone to mechanical issues.
Cost Considerations
While SSDs offer superior performance, they come at a higher cost. Here’s a breakdown:
Initial Investment
- HDD: Lower upfront cost.
- SSD: Higher upfront cost but may save money in the long run due to lower power consumption and fewer failures.
Long-Term Value
- HDD: May require more frequent replacements.
- SSD: Longer lifespan and better performance can justify the higher cost.
Use Cases for HDD Hosting
HDD hosting is suitable for:
-
- Budget-Conscious Projects: Ideal for personal blogs or small business websites.
- Large Data Storage: Suitable for storing large files, such as backups or archives.
</ul